Calculator Tutorials
How to Use a TI-84 Calculator (Step-by-Step)
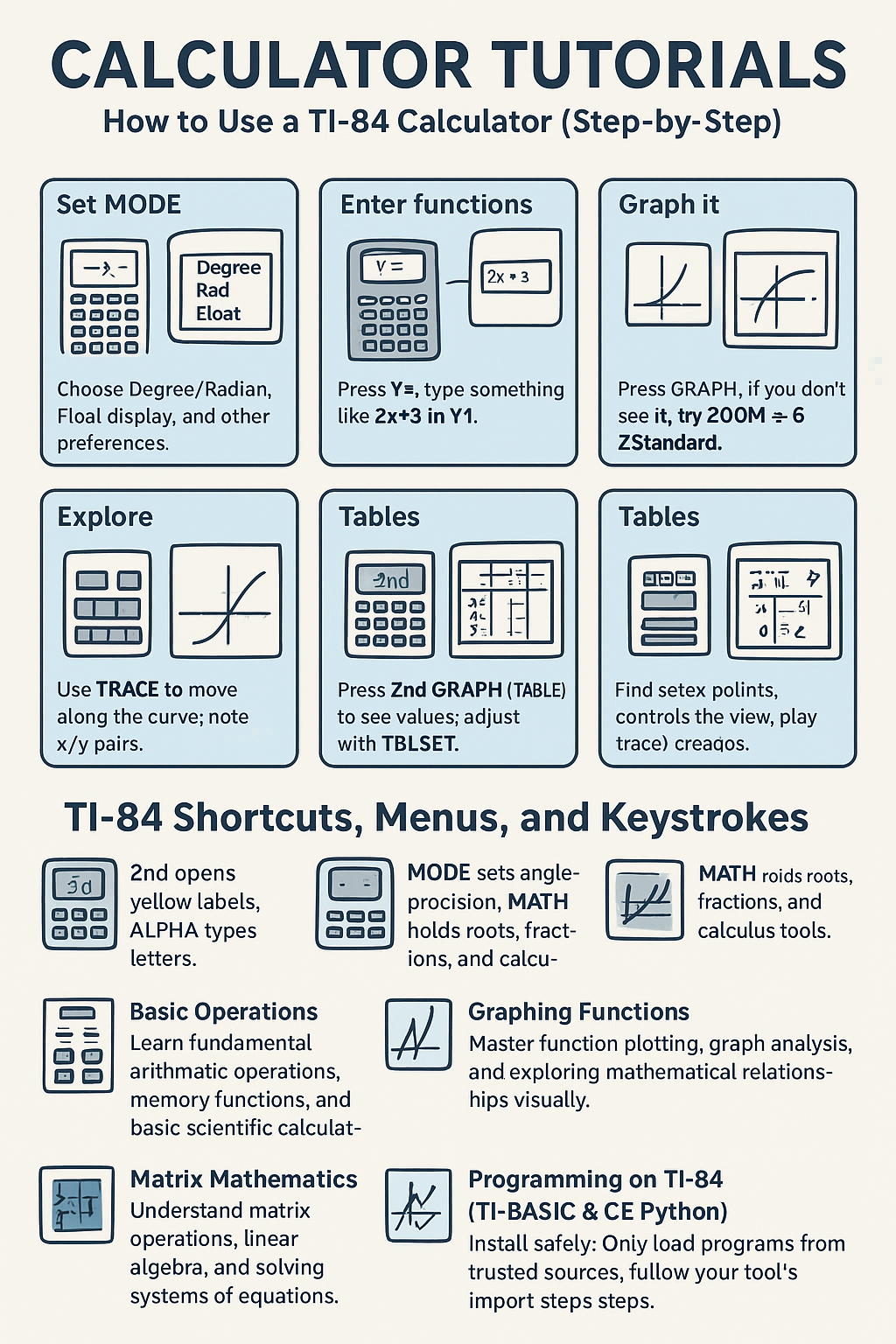
- Set MODE: Choose Degree/Radian, Float display, and other preferences.
- Enter functions: Press Y=, type something like 2x+3 in Y1.
- Graph it: Press GRAPH. If you don't see it, try ZOOM → 6: ZStandard.
- Explore: Use TRACE to move along the curve; note x/y pairs.
- Tables: Press 2nd GRAPH (TABLE) to see values; adjust with TBLSET.
- Stats in seconds: STAT → EDIT to enter lists, then STAT → CALC → 1-Var Stats (or 2-Var).
- Find key points: 2nd → CALC on the graph to locate zeros, intersections, and extrema.
TI-84 Shortcuts, Menus, and Keystrokes
- 2nd opens yellow labels; ALPHA types letters.
- MODE sets angle/precision; MATH holds roots, fractions, and calculus tools.
- STAT manages lists, stats, and regressions.
- WINDOW/ZOOM controls the view; TRACE reads exact coordinates.
Basic Operations
Learn fundamental arithmetic operations, memory functions, and basic scientific calculations.
Graphing Functions
Master function plotting, graph analysis, and exploring mathematical relationships visually.
Matrix Mathematics
Understand matrix operations, linear algebra, and solving systems of equations.
Statistics & Data
Analyze data sets, calculate statistical measures, and create data visualizations.
Programming on TI-84 (TI-BASIC & CE Python)
- Install safely: Only load programs from trusted sources; follow your tool's import steps.
- TI-BASIC demo: PRGM → NEW, name it, then add simple Prompt A, Disp A+1 lines to see flow.
- Python (CE Python): Great for loops, conditions, and math snippets; keep scripts small.
Best Practices for Algebra, Trig, Calculus, and Stats
Quadratic formula & solver tips
Graph the quadratic and use CALC → zero to verify roots. Keep WINDOW reasonable for clarity.
Derivatives (nDeriv) & integrals (fnInt)
MATH → nDeriv and fnInt can estimate slopes and areas. Use appropriate bounds and step sizes.
Hypothesis tests & confidence intervals (STAT → TESTS)
Know your test first (Z, T, χ²). Organize data in L1, L2, etc., then run the matching test.